- Offensive Techniques & Strategies
Physical Conditioning and Training

| Superior Conditioning | Preparation | Physiological Benefits | Brain Boosting Benefits |
Superior Conditioning
Superior conditioning does not just happen nor is it acquired quickly. It is the result of a well planned and executed program of exercise, rest, and diet. Training is exacting, and the responsibility is heavy. What is done off the court is as important as what is done on it. To be successful, each player as well as the team collectively, must be possessed with the desire and determination to develop superior physical condition. Throughout the course of the season the team will be pushed and trained hard. However, it is going to be up to each individual to see that their maximum physical condition is achieved and maintained. Anything less is a violation of a trust.

Physiological Objectives
To improve the efficiency of the cardio-respiratory system (aerobic capacity).
To delay fatigue and decrease recovery time (anaerobic capacity).
To increase general strength and muscle tone.
Exercise Within Your Tolerance
Have patience and do not rush your training program. It is important to work up to strenuous exercise. Avoid straining and pushing yourself to the extent that you become over fatigued.
Overexertion is dangerous to your health and defeats the conditioning program. Instead of feeling fit and vivacious, you will feel chronically tired and listless.
Symptoms of overexertion are chest pains, severe breathlessness, dizziness, loss of muscle control and nausea. If you experience any of these symptoms stop exercising.

Proper Preparation
Warm-Up


The warm-up period for basketball should be composed mainly of flexing and stretching exercises. It should be of sufficient duration (approximately ten minutes) and intensity to adequately prepare yourself for the physical demands of the game or work-out.
Try not to expend yourself during the warm-up periods. The purpose of a warm-up is to prepare for muscular activity and is not an exhausting activity to bring on fatigue.
In performing the various stretching exercise, it is important to warm-up the entire body. Surface or local warming-up of specific limbs will result in earlier fatigue and will also lessen work output. Do not hold your breath or force muscles beyond their capabilities. Stretch -- do not bounce. Flexibility will increase with time.
Cooling Down
After practice, be sure to ease the transition between running and resting by walking or slow jogging for at least five (5) minute. Taper off gradually. A sudden stop can cause dizziness, fainting, cramps, or even more serious consequences.

 The Importance of Cooling Down
The Importance of Cooling DownExercise Regularly
After absence or injury be patient and do not try to catch up over night. Stay within your tolerance.

Physiological Benefits of Conditioning
1. Increases oxygen consumption.
Breath larger amounts of air at a slower rate.
Strengthens respiratory muscles increasing endurance and reducing resistance.
Increases utilization of oxygen.2. Increases the cardiac output.
Heart pumps more blood per beat.
Reduces work load on the heart.3. Increases circulation.
Improves general circulation.
Increases the number of red blood cells and amount of hemoglobin in the blood.4. Increases the ability to use energy sources.
Use of energy sources is increased.
Replenishes energy stores at a faster rate (recovery).
Increases tolerance to high levels of lactic acid (fatigue).5. Increases muscle strength and tone.
Reduces injuries with added alertness and strength.
Increases performance.
Prolongs the number of years of athletic performance.

Conditioning & Learning

There may be much more to being in shape than just gaining a physical advantage. Breaking a sweat on a regular basis can get you into amazing shape, but new research has shown it can make you smarter too. Physical workouts will not only increase your muscular, respiratory and cardiovascular capabilities, it will also improve your smarts and productivity. Even a 30 minute workout pumps extra blood to the brain, delivering vital oxygen and nutrients it requires to perform at maximum efficiency. Cardiovascular workouts provide the brain with chemicals that enhance functions such as memory, problem solving and decision making. All which are critical to a successful basketball performance.
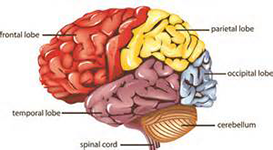
Working Out the Brain at the Same Time as Your Heart
According to clinical psychologist and memory researcher, Thomas Crook, PH. D, “cardiovascular health is more important than any other single factor in preserving and improving learning and memory. During exercise, all that extra blood bathes your brain cells with oxygen and glucose which they need to function. The more oxygen the brain gets, the better it performs.”
Muscles also send hormones to your brain.
These hormones mix with a chemical, called brain-derived neurotrophic factor or BDNF, play a role in brain cell growth, mood regulation and learning. BDNF is like fertilizer for the brain. Without it, our brains can’t take in new information or make new cells. Exercise has another vital role in signaling the release of several key hormones that not only affects learning and attention, but also influences attention, perception and motivation. By elevating these hormones in the brain, it helps keeps us in focus, feeling better and releases tension.”
Importance of Practicing at Game Speed
Intensity of the workout makes a difference. A study of Learning and Memory has found that people learned vocabulary words 20% faster after intense exercise than after low-intense exercising. Those who under take a more demanding exercise, experienced higher levels of BDNF, dopamine and epinephrine in their brains afterwards. Therefore, the more you challenge your body physically, the more the brain benefits. By being in great physical shape, it will not only allow you to play harder and faster for longer periods of time but will also enable you to think quicker and make better decisions.
© 2026 HoopTactics All Rights Reserved.
